13.3.2. The 30°-60°-90° Triangle
In a 30°-60°-90° right triangle, the length of the hypotenuse is twice the length of the shorter leg (side opposite the 30° angle) and the length of the longer leg (side opposite the 60° angle) is sqrt(3) times the length of the shorter leg. So, if we consider a 30°-60°-90° triangle with length of shorter leg equal to 1 unit; longer leg must be equal to sqrt(3) and hypotenuse equal to 2. Using this triangle and SOHCAHTOA, the EXACT VALUES of the six trigonometric ratios for 30° or π/6 and 60° or π/3 are calculated as follows:
cos 30° = sin 60° = sqrt(3) / 2
sec 30° = csc 60° = 2/3 sqrt (3)
sin 30° = cos 60° = 1/2
csc 30° = sec 60° = 2
tan 30° = cot 60° = sqrt(3) / 3
cot 30° = tan 60° = sqrt(3)
Now, let us use the app to find these values.
Calculate:
1) cos 30°
2) sin 30°
3) tan 30°
4) sec 30°
5) csc 30°
6) cot 30°
Calculator Solutions
Enter each trigonometric ratio as it appears.
Type one ratio per line.
Add degree symbol after typing the angle measure.
Alternatively, activate the DEG unit by tapping the DEG-RAD button on the upper right of the calculator display.
If you want to use π/6 , make sure that the DEG-RAD button is swift to RAD.
Use the app to find the exact value of the following trigonometric ratios:
7) cos 60°
8) sin 60°
9) tan 60°
10) sec 60°
11) csc 60°
12) cot 60°
Calculator Solutions
Enter each trigonometric ratio as it appears.
Type one ratio per line.
Add degree symbol after typing the angle measure.
Alternatively, activate the DEG unit by tapping the DEG-RAD button on the upper right of the calculator display.
If you want to use π/3 , make sure that the DEG-RAD button is swift to RAD.
Multiples of 30° and 60°
Now let us use these two special angles, 30° and 60°, to find the exact trigonometric value of some of its multiples.
Examples
Find the exact value of each trigonometric ratio below.
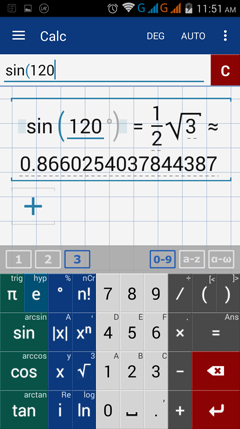
1) sin 120°
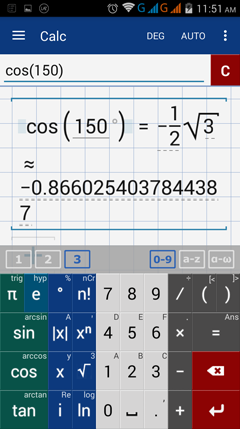
2) cos 150°
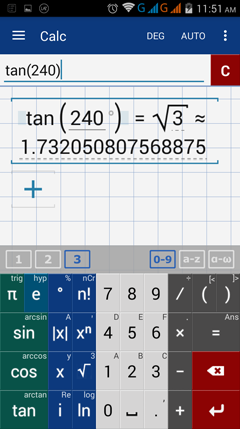
3) tan 240°
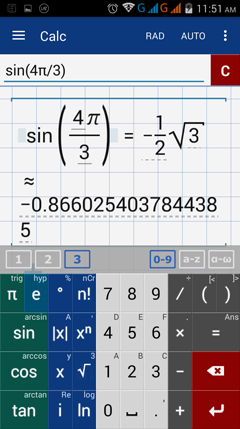
4) sin 4π/3
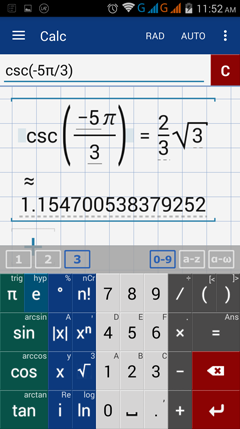
5) csc (-5π/3)
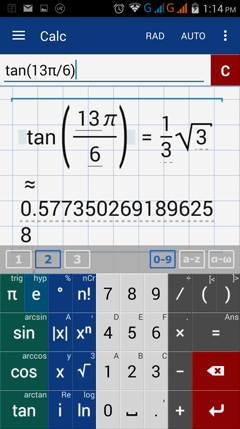
6) tan (13π/6)
Calculator Solutions
1) Enter sine by tapping sin key once. Type 120. Add the degree symbol.
Note: The terminal side of a 120° lies in quadrant II. The sine value is positive.
2) Enter cosine by tapping cos key once. Type 150. Add the degree symbol.
Note: The terminal side of a 150° lies in quadrant II. The cosine value is negative.
Note: The terminal side of a 150° lies in quadrant II. The cosine value is negative.
3) Enter tangent by tapping tan key once. Type 240. Add the degree symbol.
Note: The terminal side of a 240° lies in quadrant III. The tangent value is positive.
Note: The terminal side of a 240° lies in quadrant III. The tangent value is positive.
4) Tap DEG button to swift to RAD.
Enter sine by tapping sin key once.
Type 4. Add the pie symbol.
Enter fraction bar. Type 3
Note: The terminal side of a central angle whose intercepted arc measures 4π/3 lies in quadrant III. The sine value is positive.
Enter sine by tapping sin key once.
Type 4. Add the pie symbol.
Enter fraction bar. Type 3
Note: The terminal side of a central angle whose intercepted arc measures 4π/3 lies in quadrant III. The sine value is positive.
5) Tap DEG button to swift to RAD.
Enter sine by tapping sin key once.
Type negative 5. Add the pie symbol.
Enter fraction bar. Type 3
Note: The terminal side of a central angle rotated clockwise and whose intercepted arc measures 5π/3 lies in quadrant I.
The cosecant value is positive.
Enter sine by tapping sin key once.
Type negative 5. Add the pie symbol.
Enter fraction bar. Type 3
Note: The terminal side of a central angle rotated clockwise and whose intercepted arc measures 5π/3 lies in quadrant I.
The cosecant value is positive.
6) Tap DEG button to swift to RAD.
Enter tangent by tapping tan key once.
Type negative 13. Add the pie symbol.
Tap fraction bar. Type 6
Enter tangent by tapping tan key once.
Type negative 13. Add the pie symbol.
Tap fraction bar. Type 6