15.10. Limit of a Piecewise Function
A piecewise function behaves differently in different intervals of its domains. One example of a piecewise function is the absolute value function. An absolute value function increases when x > 0 and is equal to x. It also increases when x < 0 and is equal to -x.
Due to the nature of piecewise functions, the graph of f(x) may have discontinuities. There are multiple cases for finding the limit of a piecewise function. If x = c is inside an interval but is not a restricted value, the limit is f(c). If x = c is at a restricted value or where the function changes behaviors, consider both left- and right-hand limits.
Illustrative Example
Refer to the given function f(x) to evaluate each limit.
Solutions
Calculator solution
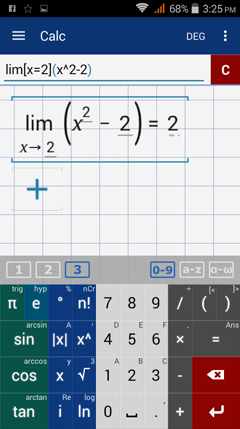
Since x = 2 is in the interval x > 0, plug 2 into f(x) = x^2 - 2. The limit is f(2) = 2^2 - 2 = 2.
Type in: lim [ x = 2 ] ( x^2 - 2 )
Since x = 2 is in the interval x > 0, plug 2 into f(x) = x^2 - 2. The limit is f(2) = 2^2 - 2 = 2.
Type in: lim [ x = 2 ] ( x^2 - 2 )
Calculator solution
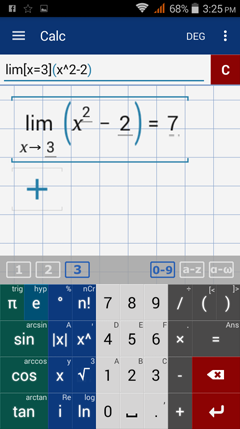
Since x = 3 is in the interval x > 0, plug it into the function f(x) = x^2 - 2. The limit is f(3) = 3^2 - 2 = 7.
Type in: lim [ x = 3 ] ( x^2 - 2 )
Since x = 3 is in the interval x > 0, plug it into the function f(x) = x^2 - 2. The limit is f(3) = 3^2 - 2 = 7.
Type in: lim [ x = 3 ] ( x^2 - 2 )
Calculator solution
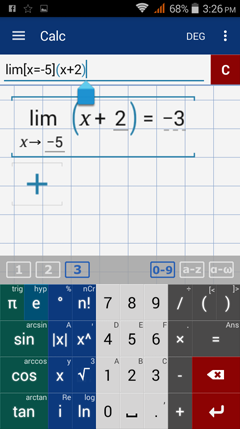
Since x = -5 is in the interval x < 0, plug in -5 into the function f(x) = x + 2. The limit is f(-5) = -5 + 2 = -3.
Type in: lim [ x = -5 ] ( x + 2 )
Since x = -5 is in the interval x < 0, plug in -5 into the function f(x) = x + 2. The limit is f(-5) = -5 + 2 = -3.
Type in: lim [ x = -5 ] ( x + 2 )
Calculator solution
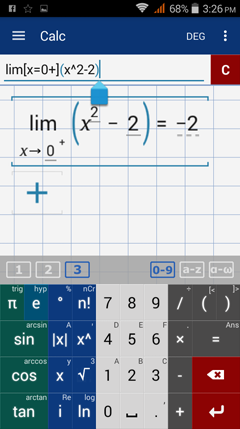
Although the function changes behavior around 0, we are looking for the right-hand limit. Because x approaches 0 from the right, we plug 0 into the function f(x) = x^2 - 2. The limit is f(0) = 0^2 - 2 = -2.
Type in: lim [ x = 0 + ] ( x^2 - 2 )
Although the function changes behavior around 0, we are looking for the right-hand limit. Because x approaches 0 from the right, we plug 0 into the function f(x) = x^2 - 2. The limit is f(0) = 0^2 - 2 = -2.
Type in: lim [ x = 0 + ] ( x^2 - 2 )
Because the function changes behavior around 0, we have to consider the left- and right-hand limits.
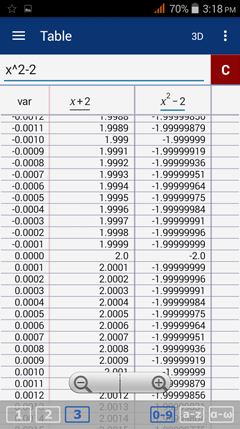
Solution 1: Table
x -0.01 -0.001 -0.001 -0.0001 -0.00001 0 0.00001 0.0001 0.001 0.01
f(x) 1.99 1.999 1.9999 1.99999 1.999999 2 -1.999999999 -1.99999999 -1.999999 -1.9999
Since f(x) approaches 2 from the left and -2 from the right, the limit of f(x) does not exist.
Solution 1: Table
x -0.01 -0.001 -0.001 -0.0001 -0.00001 0 0.00001 0.0001 0.001 0.01
f(x) 1.99 1.999 1.9999 1.99999 1.999999 2 -1.999999999 -1.99999999 -1.999999 -1.9999
Since f(x) approaches 2 from the left and -2 from the right, the limit of f(x) does not exist.
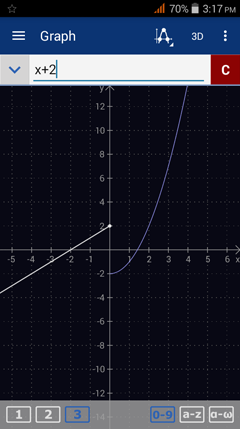
Solution 2: Graphing
Sketch the graph of f(x). Because the graph has a jump discontinuity at x = 0, the limit as x approaches 0 does not exist.