1.4. Input, Enter, Delete, Clear and UNDO Buttons
Input
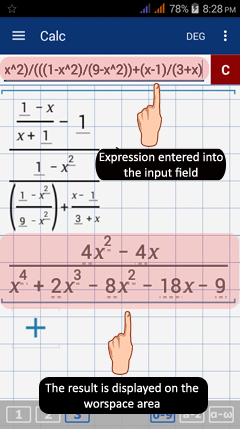
Type in the expression/equation into the input field.
The expression and result are displayed automatically on the workspace area as you type. See the example below.
Type in the expression/equation into the input field.
The expression and result are displayed automatically on the workspace area as you type. See the example below.
Enter Button
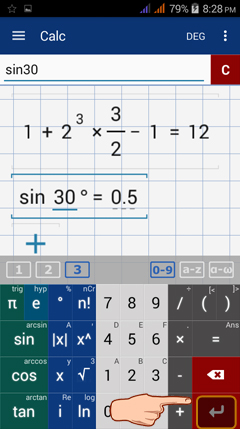
Tap the enter button to type in a new expression or equation.
Delete Button
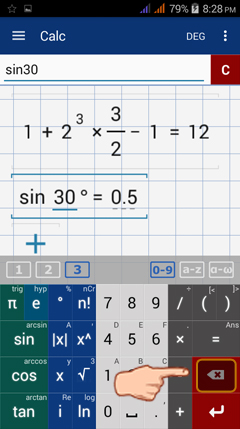
Tap or hold the delete button (as highlighted below) is below the = / ans button and above the enter button in the lower right-hand corner of the keyboard. Hold it until all characters are deleted. If you only want to delete one or two characters, tap it according to the number of characters to delete.
Clear Button
Tap the clear button next to the input field to clear an expression.
Hold it to erase all expressions displayed in the workspace area.
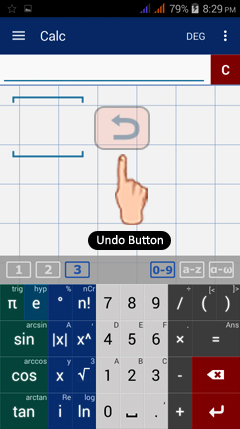
Undo Button
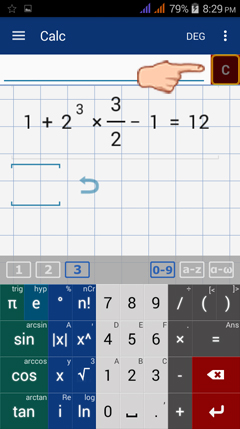
The undo button allows you to restore the previous equation or expression you deleted. This button appears on the calculator screen area only after you have deleted a character (term, constant, expression or equation) using the clear button (tapped only once). Shown below is what the undo button will look like:
Note: If you tap and hold the clear button, the undo button won't appear on the screen. It will only appear after you've tapped the clear button once since it will only undo the final step in the last equation or expression that was entered.
To undo the last expression/equation deleted, tap the undo button on the screen. Once tapped, the last expression/equation will automatically appear in the input field and in the workspace area.
Illustrative Example
Evaluate the expression 4x^2 - 3x + 5 using the value of x in the equation 3(x - 2) + 3x = 12 - 5x.
Calculator Solution
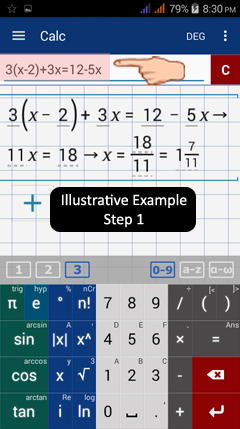
1) Type the equation 3(x - 2) + 3x = 12 - 5x using the math keyboard (default calculator keyboard).
To undo the last expression/equation deleted, tap the undo button on the screen. Once tapped, the last expression/equation will automatically appear in the input field and in the workspace area.
Illustrative Example
Evaluate the expression 4x^2 - 3x + 5 using the value of x in the equation 3(x - 2) + 3x = 12 - 5x.
Calculator Solution
1) Type the equation 3(x - 2) + 3x = 12 - 5x using the math keyboard (default calculator keyboard).
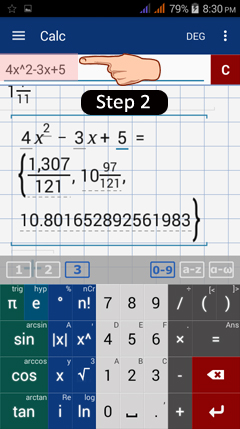
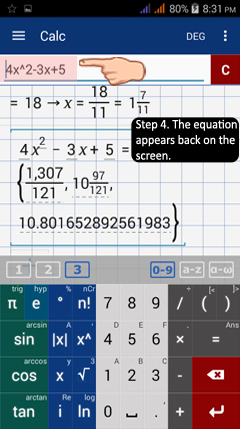
2) Type in 4x^2 - 3x + 5.
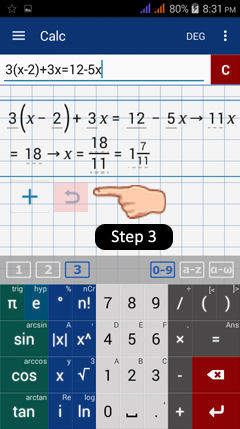
3) Now, suppose that after typing in 4x^2 - 3x + 5, you accidentally hit the clear button but want to restore the expression without having to enter it again.
Because you hit the clear button only once, you will have the option to use the undo button as shown below in the workspace area. Tap the undo button to restore the previously deleted expression.
4) Once using the undo button, the deleted expression 4x^2 - 3x + 5 will reappear in both the input field and the workspace area.